飞凌 OK113i-C 全志T113-i开发板 CAN 通信C代码测试
-
飞凌官方手册中关于CAN测试部分使用的是命令行进行的简单测试,实际开发过程中还是要使用C代码去操作CAN设备,本帖主要讲解怎么使用C代码对CAN设备进行读写的收发操作。
First of all ,先查看所有网卡信息,看看板上是否有CAN设备网络:
root@ok113i:/# ifconfig -a can0 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 NOARP MTU:16 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:10 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B) can1 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 NOARP MTU:16 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:10 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B) Interrupt:1 eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr BA:E9:F2:1C:9D:87 inet addr:192.168.0.232 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::b8e9:f2ff:fe1c:9d87/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:421 errors:0 dropped:14 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:9 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:27272 (26.6 KiB) TX bytes:726 (726.0 B) Interrupt:39 ip6tnl0 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 NOARP MTU:1452 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B) sit0 Link encap:IPv6-in-IPv4 NOARP MTU:1480 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B) wlan0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 2C:C3:E6:67:4D:3B BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)1. CAN组网前的准备,设置CAN通信服务的通信速率。
使用如下命令分别设置CAN0和CAN1的通信速率:
root@ok113i:/home/forlinx# ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 500000 [ 4075.425084] IPv6: ADDRCONF(NETDEV_CHANGE): can0: link becomes ready root@ok113i:/home/forlinx# ip link set can1 up type can bitrate 500000 [ 4086.037967] IPv6: ADDRCONF(NETDEV_CHANGE): can1: link becomes ready以上设置can0 和 can1 通信速率均为500kbps,这个速率值务必记住,所有接入组网的的can节点都是以这个速率通信。
2. 使用C语言写一个CAN通信的发送接收测试程序,主要验证CAN发送和接收数据是否正常。
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <signal.h> #include <string.h> #include "can_apply.h" #define MASTR_CAN1_ID 0x100 #define MASTR_CAN2_ID 0x101 #define RX_MSG_NUM 16 #define MAX_BUF_LEN 64 typedef enum { CAN_1, CAN_2, CAN_RES }can_type; typedef struct{ int can_id; unsigned char can_dlc; unsigned char data[MAX_BUF_LEN]; }can_msg_t; static int bexit = 0; static int can0_sock,can1_sock; can_msg_t can_rx_msg[RX_MSG_NUM]; unsigned int can1_id = 0; unsigned int can2_id = 0; void signal_handler(int signo) { printf("signal %d(%s) received\n", signo, strsignal(signo)); bexit = 1; } int can_send_data(can_type type, unsigned char *buf, int len) { int i, j; int cnt; int sock; int ret = 0; struct can_frame frame; if(type == CAN_1) { sock = can0_sock; frame.can_id = can1_id; } else { sock = can1_sock; frame.can_id = can2_id; } for(i = 0; i < len; i += 8) { cnt = len - i; if(cnt > 8) frame.can_dlc = 8; else frame.can_dlc = cnt; for(j=0; j<frame.can_dlc; j++) { frame.data[j] = buf[i+j]; } if(can_send(sock, frame) < 0) { ret = -1; break; } } return ret; } void can_recv_data(int sock) { static unsigned char tail = 0; int i; int can_id; unsigned char can_dlc; unsigned char *data; struct can_frame frame; int index = can0_sock == sock ? 0 : 1; if(can_recv(sock, &frame) < 0) return ; can_id = frame.can_id; can_dlc = frame.can_dlc; data = frame.data; printf("CAN%d dlc = %d, can_id = %x\ndata:", index,frame.can_dlc, frame.can_id); for(i=0; i<frame.can_dlc; i++) printf("0x%02x ", frame.data[i]); printf("\n"); } void *can_proc_start(void *arg) { int nready; int maxfd; fd_set readfds; int sock = *(int *)arg; FD_ZERO(&readfds); FD_SET(sock, &readfds); maxfd = sock; while(!bexit) { nready = select(maxfd+1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, NULL); if(nready < 0) { perror("can select"); break; } else if(nready == 0) { continue; } /* data is ready */ if(FD_ISSET(sock, &readfds)) { can_recv_data(sock); } else { ; } } close(sock); pthread_detach(pthread_self()); pthread_exit(0); } // 初始化CAN0和CAN1设备,并创建两个接收数据处理线程 static void can_sock_init() { pthread_t tid; can0_sock = can_open("can0"); if(can0_sock < 0) return ; can1_sock = can_open("can1"); if(can1_sock < 0) return ; if (0 != pthread_create(&tid, NULL, can_proc_start, (void *)&can0_sock)) { return ; } if (0 != pthread_create(&tid, NULL, can_proc_start, (void *)&can1_sock)) { return ; } can1_id = MASTR_CAN1_ID; can2_id = MASTR_CAN2_ID; printf("can open sucess can0_sock:%d, can1_sock:%d\n", can0_sock, can1_sock); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { char *send_data = "hello,can!"; signal(SIGINT, signal_handler); signal(SIGPIPE, signal_handler); signal(SIGTERM, signal_handler); can_sock_init(); // 初始化CAN0和CAN1设备数据,并创建接收线程 do { sleep(1); can_send_data(CAN_1, (unsigned char *)send_data, strlen(send_data) - 1); } while (!bexit); return 0; }测试程序主要实现了如下功能:
- 建立两个接收数据线程接收CAN设备的数据并打印CAN网络上的数据。
- 通过CAN0设备定时1秒发送一串"hello,can!"数据到CAN网络。
3. 运行并验证程序功能。
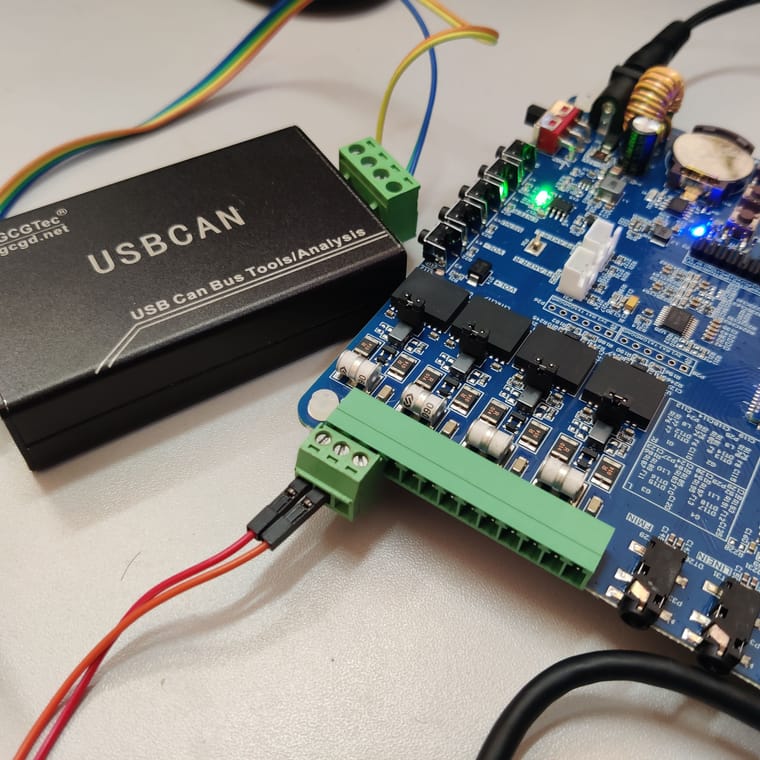
PC上使用CAN分析工具按下图接好线
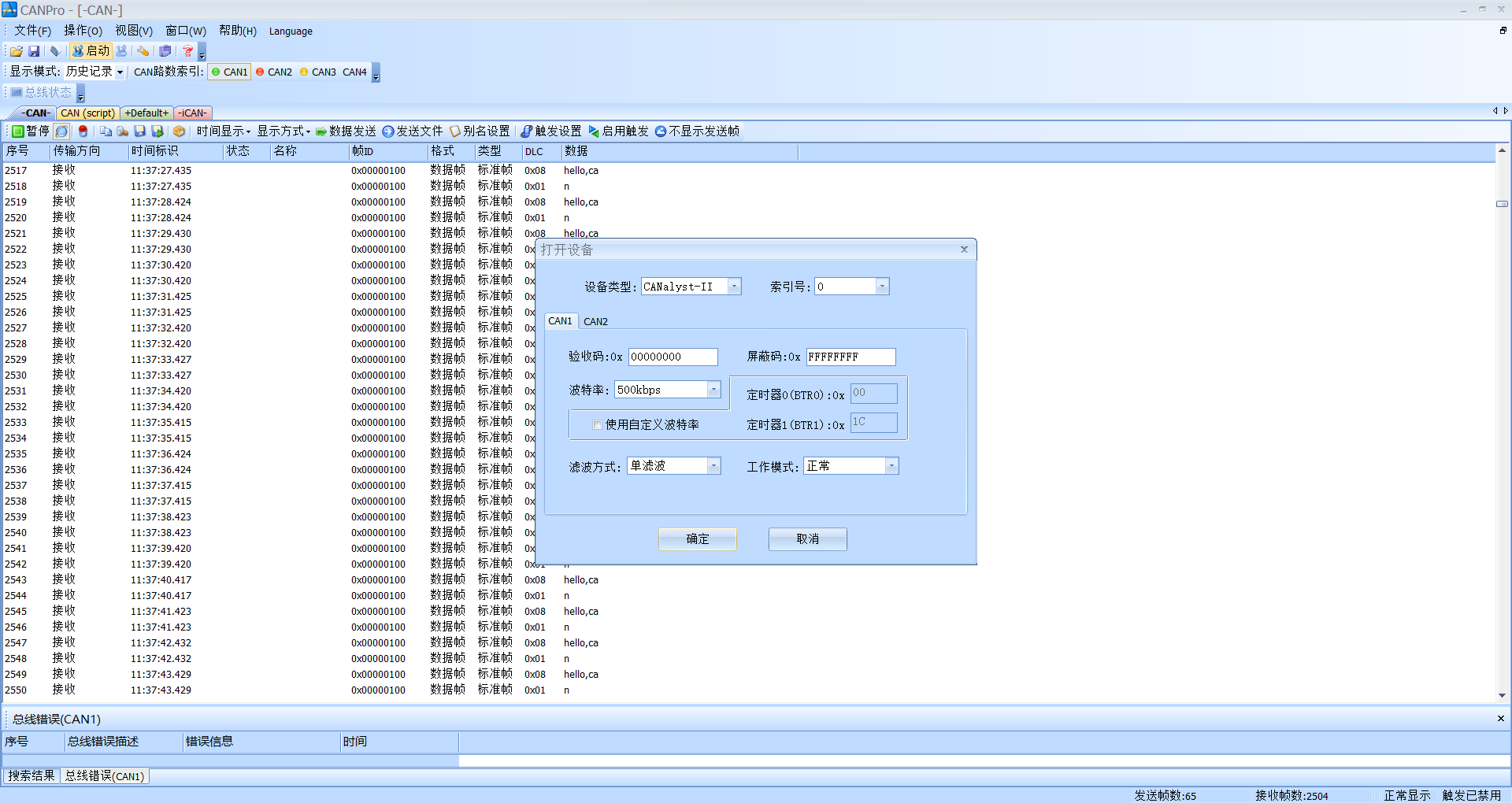
打开CAN调试软件,配置成500kbps的速率并打开设备,如下:
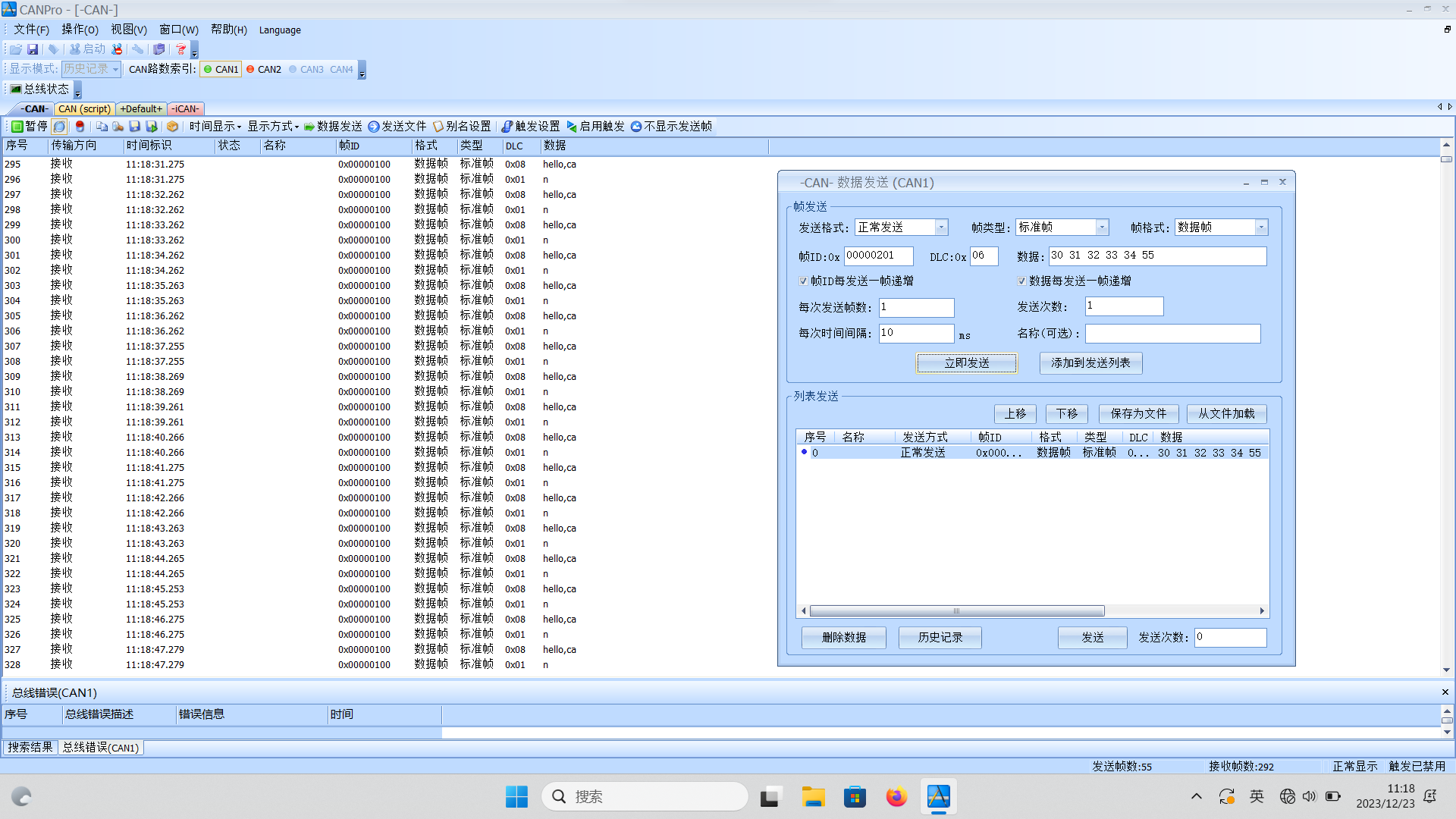
使用CAN调试软件给设备发送数据,如下:
将编译好的程序上传到板子上并运行,以下是正常收到数据后程序的打印信息:
root@ok113i:/home/forlinx# ./can_test can open sucess can0_sock:3, can1_sock:4 ## PC往CAN0口发送测试数据接收打印 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN0 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 ## PC往CAN1 口发送测试数据接收打印 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55 CAN1 dlc = 6, can_id = 201 data:0x30 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x55测试程序工程结构
├── build # 编译目录 ├── can_apply.c # CAN 操作简单封装C源码 ├── can_apply.h # CAN 操作简单封装头文件 ├── CMakeLists.txt # cmake 编译规则文件 ├── cross-t113-i.cmake # CMake嵌入式交叉编译工具链文件 └── main.c # 测试程序主体源代码工程源代码编译
cd build cmake .. -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../cross-t113-i.cmake make Scanning dependencies of target can_test [ 33%] Building C object CMakeFiles/can_test.dir/main.c.o [ 66%] Building C object CMakeFiles/can_test.dir/can_apply.c.o [100%] Linking C executable can_test [100%] Built target can_test工程使用cmake进行编译,需要注意的是要根据实际情况修改
cross-t113-i.cmake中的GCC交叉编译工具的路径。# # CMake Toolchain file for crosscompiling on ARM. # # This can be used when running cmake in the following way: # cd build-t113/ # cmake .. -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../cross-t113-i.cmake # or set(CROSS_PATH /home/luoyang/Dev/sdk/T113-i/OK113i-linux-sdk/out/t113_i/ok113i/longan/buildroot/host) # Target operating system name. set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Linux) set (CMAKE_C_FLAGS "-std=gnu11" CACHE STRING "Set C Compiler Flags" FORCE) # Name of C compiler. set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER "${CROSS_PATH}/bin/arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc") set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "${CROSS_PATH}/bin/arm-linux-gnueabi-g++") set (CMAKE_C_FLAGS "-std=gnu11 -mcpu=cortex-a7 -mfloat-abi=softfp -mfpu=neon-vfpv4 -mno-unaligned-access -fno-aggressive-loop-optimizations -ffunction-sections" CACHE STRING "Set C Compiler Flags" FORCE) set (CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-mcpu=cortex-a7 -mfloat-abi=softfp -mfpu=neon-vfpv4 -mno-unaligned-access -fno-aggressive-loop-optimizations -ffunction-sections" CACHE STRING "Set C++ Compiler Flags" FORCE) # link flags set(CMAKE_LINK_FLAGS "${CMAKE_LINK_FLAGS} -mcpu=cortex-a7 -mfloat-abi=softfp -mfpu=neon-vfpv4 -mno-unaligned-access -fno-aggressive-loop-optimizations" CACHE STRING "Set link Flags" FORCE) SET(CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR "armv7-a_hardfp") add_definitions(-fPIC) add_definitions(-DARMLINUX) add_definitions(-D__gnu_linux__) # Where to look for the target environment. (More paths can be added here) set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH "${CROSS_PATH}/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabi/sysroot") # Adjust the default behavior of the FIND_XXX() commands: # search programs in the host environment only. set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_PROGRAM NEVER) # Search headers and libraries in the target environment only. set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_LIBRARY ONLY) set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_INCLUDE ONLY)测试工程源代码
can-test.tar.gz -
Copyright © 2024 深圳全志在线有限公司 粤ICP备2021084185号 粤公网安备44030502007680号