【XR806开发板试用】基于MQTT实现手机与XR806互联——XR806开发板开发部分
-
-
小项目背景
鸿蒙系统也听说发布一段时间了,一直没去了解。但是勒,既然是华为发布的项目,还是想找个时间了解下的。刚好在公众号看到免费申请鸿蒙开发板试用,那就顺便学习下吧。
鸿蒙系统的特点是万物互联,那么申请的开发板我也准备用来做一个物联网小项目,至于做啥呢?...思量许久,感觉无论用来物联网控制啥东西,都需要额外成本,那就暂时放弃外设控制的想法,先完成简单的Android手机与开发板通过MQTT互联吧。 -
简述
本项目主要涉及如下方面:- XR806的单片机固件开发
XR806的开发主要涉及鸿蒙LiteOS、XR806本身的SDK包、MQTT,在本贴中,会较详细地讲述。
在MQTT的实现上,我一直在纠结,本人之前开发单片机程序的时候其实是没接触过LWIP和MQTT这部分涉及到嵌入式网络相关的,因此在开发前是有一部分时间去了解MQTT的,目前我看到鸿蒙相关的开发板都是使用基于Paho的开源MQTT(可能是我没找到其他的哈),但是我发现LWIP本身是有实现MQTT客户端的源码的,既然如此,为啥不直接用LWIP本身的呢?MQTT是应用层的协议,因此移植其实特别简单,基于传输层的TCP移植就ok了。不过,如果是使用LWIP本身实现的MQTT,那很可能连移植都不需要去做,因此,我打算直接使用LWIP内部的MQTT客户端实现。 - Android的App开发
Android的开发也很简单,主要是搭建个简单的界面,并通过开源的MQTT库实现MQTT客户端。本贴中也会讲述这部分内容。
本贴中,Android的MQTT是基于Paho的开源库实现的。
- XR806的单片机固件开发
-
整体框架
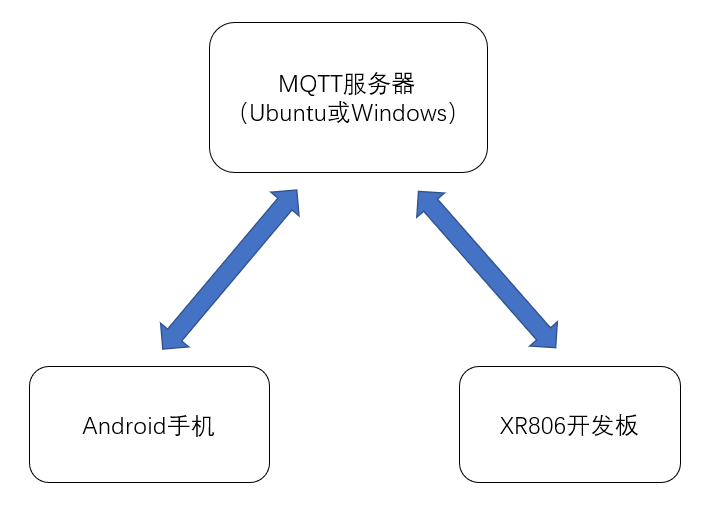
如上图,项目实现的MQTT的传输流程便是如此。本贴是在Ubuntu搭建的MQTT服务器,Android手机订阅“sensor_data”主题的消息,并且会发送“sensor_cmd”主题的信息;XR806订阅“sensor_cmd”主题的信息,并且会发送定时发送“sensor_data”的信息,这样就达到一个Android手机用户获取传感器数据并且还能实现控制设备(比如控灯)的目的。 -
XR806开发
- 鸿蒙系统的了解
关于鸿蒙的源码如何编译,恩...还是自行查资料吧,其实个人感觉这个编译系统类似android的编译,初学者多踩踩坑是可以很容易上手的。
通过查看鸿蒙的官网资料,在这里说下本人的一些理解:
首先,像XR806这种单片机开发板使用的是鸿蒙的轻量型系统(LiteOS_m),鸿蒙还有小型系统和标准系统,小型系统应该是用在imx6ull这种级别的芯片上,而标准系统就是用在手机芯片这种级别。
既然我们用的是LiteOS_m,那么就把关注范围缩小到LiteOS_m上,主要是LiteOS_m的内容比较少。
我们先看鸿蒙的目录结构,如下:
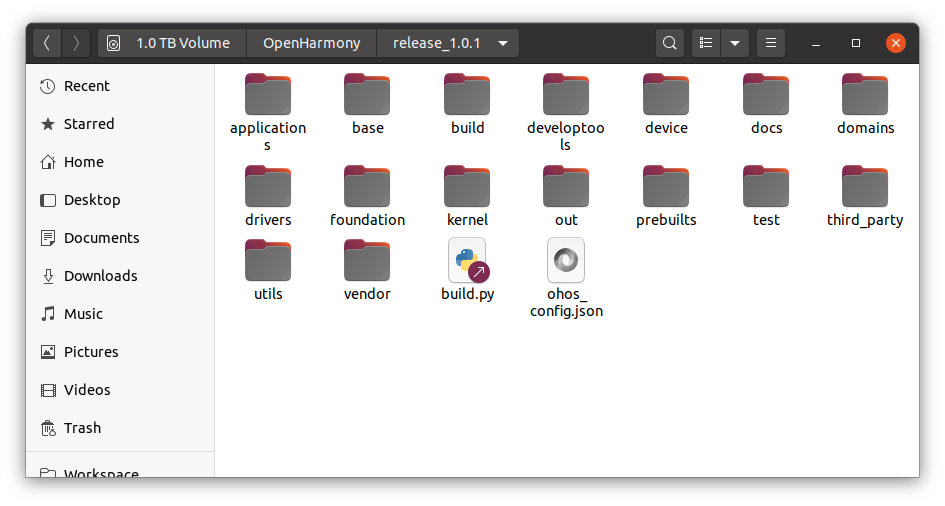
通过这个目录,我们其实大致可以猜到以下(仅提供参考):
-- applications是存放应用的位置;
-- driver应该是存放驱动的位置,但其实和我们无关,因为该目录存放的是针对小型系统(LiteOS_a)的驱动(HDI接口);
-- base存放鸿蒙系统中无关平台无关硬件的通用基础构成(不包含内核),比如基本外设的中间件接口、关于安全的源码、代码升级相关的源码,当然,可能并不适用于LiteOS_m系统,或者说不全适用;
-- build和developtools存放编译系统源码工具和开发相关工具;
-- device应该是存放具体不同设备的特定源码,也就是不同的设备型号需要适配的部分;
-- vendor应该要存放不同厂商芯片的特定源码,也就是不同系列芯片需要适配的部分;
-- out目录存放编译输出文件;
-- third_party存放第三方源码和库;
理论上,通过鸿蒙系统可以实现:无论哪个系列的芯片,哪个型号的设备,只要适配了鸿蒙系统,那么编写出来的应用程序就是通用的。
这是因为鸿蒙在应用和具体厂商设备之间提供了中间层,因此,对于应用层来说,如果底层适配完成,只需要调用中间层的通用api即可,底层硬件和应用业务逻辑分开。
这里举一个例子,比如说鸿蒙系统LiteOS_m基本外设的使用,我们可以随便打开applications目录下的一个例程,我这里打开目录“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/applications/sample/wifi-iot/app/iothardware”下的"led_example"例程,主要相关源码如下:
static void *LedTask(const char *arg) { (void)arg; while (1) { switch (g_ledState) { case LED_ON: IoTGpioSetOutputVal(LED_TEST_GPIO, 1); usleep(LED_INTERVAL_TIME_US); break; case LED_OFF: IoTGpioSetOutputVal(LED_TEST_GPIO, 0); usleep(LED_INTERVAL_TIME_US); break; case LED_SPARK: IoTGpioSetOutputVal(LED_TEST_GPIO, 0); usleep(LED_INTERVAL_TIME_US); IoTGpioSetOutputVal(LED_TEST_GPIO, 1); usleep(LED_INTERVAL_TIME_US); break; default: usleep(LED_INTERVAL_TIME_US); break; } } return NULL; }可以看到,控制IO口是通过IoTGpioSetOutputVal函数API实现的,该函数其实就是在“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/base/iot_hardware/peripheral/interfaces/kits
”目录下的“iot_gpio.h”声明的,在该目录下还能看到其它基本外设API的声明头文件。
那IoTGpioSetOutputVal函数是在哪里定义具体实现的呢?这个就是根据不同设备不同平台其实现是可能不同的,因此该函数的实现应放置在device目录下。例如hi3861的该函数实现放置在“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/device/hispark_pegasus/hi3861_adapter/hals/iot_hardware/wifiiot_lite/hal_iot_gpio.c”文件中。
当然,一个系统的适配还包括其它很多东西,比如说系统基本组件(任务、互斥量、信号量、队列等),蓝牙、wifi等具备相关协议栈的适配等等。
2. XR806的适配部分
事实上,在了解完鸿蒙系统后,再来看XR806部分的源码时,我是有点懵的。怎么个懵法呢?我从一个XR806的例程入手。我们看到“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/device/xradio/xr806/ohosdemo/iot_peripheral
”这个例子,先从入口函数来看,代码如下:void PeripheralTestMain(void) { printf("\r\nPeripheral Test Start\r\n"); if (OS_ThreadCreate(&g_main_thread, "MainThread", MainThread, NULL, OS_THREAD_PRIO_APP, 4 * 1024) != OS_OK) { printf("[ERR] Create MainThread Failed\n"); } } SYS_RUN(PeripheralTestMain);从以上代码可以看到,创建多任务使用的是OS_ThreadCreate函数。但是,看过鸿蒙开发者文档的读者都知道,鸿蒙创建多任务的API其实是LOS_TaskCreate函数,这是怎么回事呢?
其实答案很简单,XR806是在OS_ThreadCreate的函数实现中调用了LOS_TaskCreate,而且不止线程创建的接口,其他系统基础组件的接口实现都对鸿蒙的标准接口进行封装,具体在目录“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/device/xradio/xr806/os”下。这样做的目的是什么呢?我猜测可能是为了兼容以前的旧freertos项目。但这样做之后,XR806的应用程序就不能无修改跨芯片(适配完毕的)通用了,所以XR806的应用程序目录也放置在device目录下。
当然,XR806关于外设的接口实现,wifi、蓝牙的接口实现都是基于鸿蒙的标准接口的,具体可查看device相关目录。
另外一方面,XR806还将其他一些实现(即目录"OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/device/xradio/xr806/xr_skylark")编译成库了,我们在编译时,执行"make menuconfig"其实就是在进行选择编译,可以将一些不需要的实现筛选掉。对于本项目来说,需要实现mqtt需要将lwip编译进来,通过生成的.config和“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/device/xradio/xr806/liteos_m”目录下的配置文件确认,lwip已经默认编译。也可以通过编译生成的库文件确实是否有编译。
3. MQTT实现
本贴使用的MQTT基于LWIP,XR806使用的基于wifi的网络,LWIP与wifi之间应该需要做相关适配,当平台已经完成适配,暂无需关心。
因此,MQTT的实现其实很简单:第一,连接wifi热点;第二,连接MQTT服务器。前者已经有一个官方例程了,后者呢,前面已经提过基于LWIP中的MQTT来实现了。
首先将mqtt的实现源码包含进来(因为默认编译生成的lwip库没有包含应用层的实现),BUILD.gn相关源码包含如下:sources = [ "src/main.c", "//device/xradio/xr806/xr_skylark/src/net/lwip-2.1.2/src/apps/mqtt/mqtt.c", ]然后就是找到lwip的官方文档,看是否有对mqtt实现的说明文档,一看还真有,在目录“OpenHarmony/release_1.0.1/device/xradio/xr806/xr_skylark/src/net/lwip-2.1.2/doc”下。直接跟着文档走,复制——粘贴,一个简单的单片机固件即完成。当然,其实过程还是有一些坑需要查看lwip源码才能了解用法,我这里呢直接给出固件源码(比较乱,初版程序,直接堆在一个文件,还好代码量较小),也就不进行解释了,主要是我困了哈,代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "ohos_init.h" #include "kernel/os/os.h" #include "lwip/apps/mqtt.h" #include "wifi_device.h" #define WIFI_DEVICE_CONNECT_AP_SSID "Android_Sen" #define WIFI_DEVICE_CONNECT_AP_PSK "250638cks!" static OS_Thread_t g_main_thread; static OS_Thread_t g_wifi_thread; static int inpub_id; static int isConnected = 0; static int isMQTTConnected = 0; static void iot_client_do_connect(mqtt_client_t *client); static void mqtt_pub_request_cb(void *arg, err_t result); void iot_publish(mqtt_client_t *client, void *arg); /* To test the following interfaces: * IsWifiActive() * EnableWifi() * Scan() * GetScanInfoList() * AddDeviceConfig() * ConnectTo() * GetLinkedInfo() * GetDeviceMacAddress() * Disconnect() * DisableWifi() */ #define NET_IF_STATE_DBG(netif) \ do { \ if (netif_is_link_up(netif)) { \ printf("netif is up.\n"); \ } else { \ printf("netif is down.\n"); \ } \ } while (0) extern struct netif *g_wlan_netif; /* To test the following interfaces: * RegisterWifiEvent() * UnRegisterWifiEvent() */ WifiEvent sta_event; void Scan_done_deal(int state, int size) { if (state == WIFI_STATE_AVALIABLE) { printf("======== Callback: scan done, the num of bss: %d\n", size); } } void Connected_deal(int state, WifiLinkedInfo *info) { if (state == WIFI_STATE_AVALIABLE) { isConnected = 1; printf("======== Callback: connected\n"); } else if (state == WIFI_STATE_NOT_AVALIABLE) { isConnected = 0; printf("======== Callback: disconnected\n"); } } void wifi_device_connect() { printf("\n=========== Event Test Start ===========\n"); sta_event.OnWifiScanStateChanged = Scan_done_deal; sta_event.OnWifiConnectionChanged = Connected_deal; if (WIFI_SUCCESS != RegisterWifiEvent(&sta_event)) { printf("Error: RegisterWifiEvent fail\n"); return; } if (WIFI_SUCCESS != EnableWifi()) { printf("Error: EnableWifi fail\n"); return; } OS_Sleep(1); while (1) { if (!isConnected) { if (WIFI_SUCCESS != Scan()) { printf("Error: Scan fail.\n"); continue; } const char ssid_want_connect[] = WIFI_DEVICE_CONNECT_AP_SSID; const char psk[] = WIFI_DEVICE_CONNECT_AP_PSK; WifiScanInfo scan_results[30]; unsigned int scan_num = 30; if (WIFI_SUCCESS != GetScanInfoList(scan_results, &scan_num)) { printf("Error: GetScanInfoList fail.\n"); continue; } WifiDeviceConfig config = { 0 }; int netId = 0; int i; for (i = 0; i < scan_num; i++) { printf("ssid: %s ", scan_results[i].ssid); printf("securityType: %d\n", scan_results[i].securityType); if (0 == strcmp(scan_results[i].ssid, ssid_want_connect)) { memcpy(config.ssid, scan_results[i].ssid, WIFI_MAX_SSID_LEN); memcpy(config.bssid, scan_results[i].bssid, WIFI_MAC_LEN); strcpy(config.preSharedKey, psk); config.securityType = scan_results[i].securityType; config.wapiPskType = WIFI_PSK_TYPE_ASCII; config.freq = scan_results[i].frequency; break; } } if (i >= scan_num) { printf("Error: No found ssid in scan_results\n"); OS_Sleep(3); continue; } if (WIFI_SUCCESS != AddDeviceConfig(&config, &netId)) { printf("Error: AddDeviceConfig Fail\n"); } printf("Config Success\n"); if (WIFI_SUCCESS != ConnectTo(netId)) { printf("Error: ConnectTo Fail\n"); } OS_Sleep(10); } else { OS_Sleep(30); } } } static void mqtt_incoming_publish_cb(void *arg, const char *topic, u32_t tot_len) { printf("Incoming publish at topic %s with total length %u\n", topic, (unsigned int)tot_len); /* Decode topic string into a user defined reference */ if(strcmp(topic, "print_payload") == 0) { inpub_id = 0; } else if(topic[0] == 'A') { /* All topics starting with 'A' might be handled at the same way */ inpub_id = 1; } else { /* For all other topics */ inpub_id = 2; } } static void mqtt_incoming_data_cb(void *arg, const u8_t *data, u16_t len, u8_t flags) { printf("Incoming publish payload with length %d, flags %u\n", len, (unsigned int)flags); if(flags & MQTT_DATA_FLAG_LAST) { /* Last fragment of payload received (or whole part if payload fits receive buffer See MQTT_VAR_HEADER_BUFFER_LEN) */ /* Call function or do action depending on reference, in this case inpub_id */ if(inpub_id == 0) { /* Don't trust the publisher, check zero termination */ if(data[len-1] == 0) { printf("mqtt_incoming_data_cb: %s\n", (const char *)data); } } else if(inpub_id == 1) { /* Call an 'A' function... */ } else { printf("mqtt_incoming_data_cb: Ignoring payload...\n"); } } else { /* Handle fragmented payload, store in buffer, write to file or whatever */ } } static void mqtt_sub_request_cb(void *arg, err_t result) { printf("Subscribe result: %d\n", result); } static void mqtt_connection_cb(mqtt_client_t *client, void *arg, mqtt_connection_status_t status) { err_t err; if(status == MQTT_CONNECT_ACCEPTED) { printf("mqtt_connection_cb: Successfully connected\n"); /* Setup callback for incoming publish requests */ mqtt_set_inpub_callback(client, mqtt_incoming_publish_cb, mqtt_incoming_data_cb, arg); /* Subscribe to a topic named "subtopic" with QoS level 1, call mqtt_sub_request_cb with result */ err = mqtt_subscribe(client, "sensor_cmd", 1, mqtt_sub_request_cb, arg); if(err != ERR_OK) { printf("mqtt_subscribe return: %d\n", err); } iot_publish(client, NULL); } else { printf("mqtt_connection_cb: Disconnected, reason: %d\n", status); /* Its more nice to be connected, so try to reconnect */ //iot_client_do_connect(client); } } static void iot_client_do_connect(mqtt_client_t *client) { struct mqtt_connect_client_info_t ci; ip_addr_t host_ip_addr; err_t err; IP4_ADDR(ip_2_ip4(&host_ip_addr), 192, 168, 8, 105); /* Setup an empty client info structure */ memset(&ci, 0, sizeof(ci)); /* Minimal amount of information required is client identifier, so set it here */ ci.client_id = "lwip_test"; ci.keep_alive = 5; /* Initiate client and connect to server, if this fails immediately an error code is returned otherwise mqtt_connection_cb will be called with connection result after attempting to establish a connection with the server. For now MQTT version 3.1.1 is always used */ err = mqtt_client_connect(client, &host_ip_addr, 1883, mqtt_connection_cb, 0, &ci); /* For now just print the result code if something goes wrong */ if(err != ERR_OK) { printf("mqtt_connect return %d\n", err); } } /* Called when publish is complete either with sucess or failure */ static void mqtt_pub_request_cb(void *arg, err_t result) { if(result != ERR_OK) { printf("Publish result: %d\n", result); } } void iot_publish(mqtt_client_t *client, void *arg) { char pub_payload[10]= {0}; err_t err; u8_t qos = 2; /* 0 1 or 2, see MQTT specification */ u8_t retain = 0; /* No don't retain such crappy payload... */ int sensor_data = rand() % 100; sprintf(pub_payload, "%d\n", sensor_data); err = mqtt_publish(client, "sensor_data", pub_payload, strlen(pub_payload), qos, retain, mqtt_pub_request_cb, arg); if(err != ERR_OK) { printf("Publish err: %d\n", err); } } static void MainThread(void *arg) { mqtt_client_t *client = mqtt_client_new(); int count = 0; while (1) { if(client != NULL) { if (isConnected && !isMQTTConnected) { printf("connect time: %d\n", count++); iot_client_do_connect(client); } OS_Sleep(10); } } } static void WifiThread(void *arg) { wifi_device_connect(); } void IOTMain(void) { printf("\r\nIOT Sensor Start\r\n"); if (OS_ThreadCreate(&g_main_thread, "MainThread", MainThread, NULL, OS_THREAD_PRIO_APP, 4 * 1024) != OS_OK) { printf("[ERR] Create MainThread Failed\n"); } if (OS_ThreadCreate(&g_wifi_thread, "WifiThread", WifiThread, NULL, OS_THREAD_PRIO_APP, 4 * 1024) != OS_OK) { printf("[ERR] Create WifiThread Failed\n"); } } SYS_RUN(IOTMain);通过以上的程序,其实可以看到实现的逻辑就是每隔一段时间发布主题为“sensor_data”的消息,因此,我在Ubuntu上搭建好MQTT服务器后,并在Ubuntu上建立一个MQTT客户端订阅“sensor_data”主题的消息,可以定时接收到开发板发送过来的消息。效果如下:
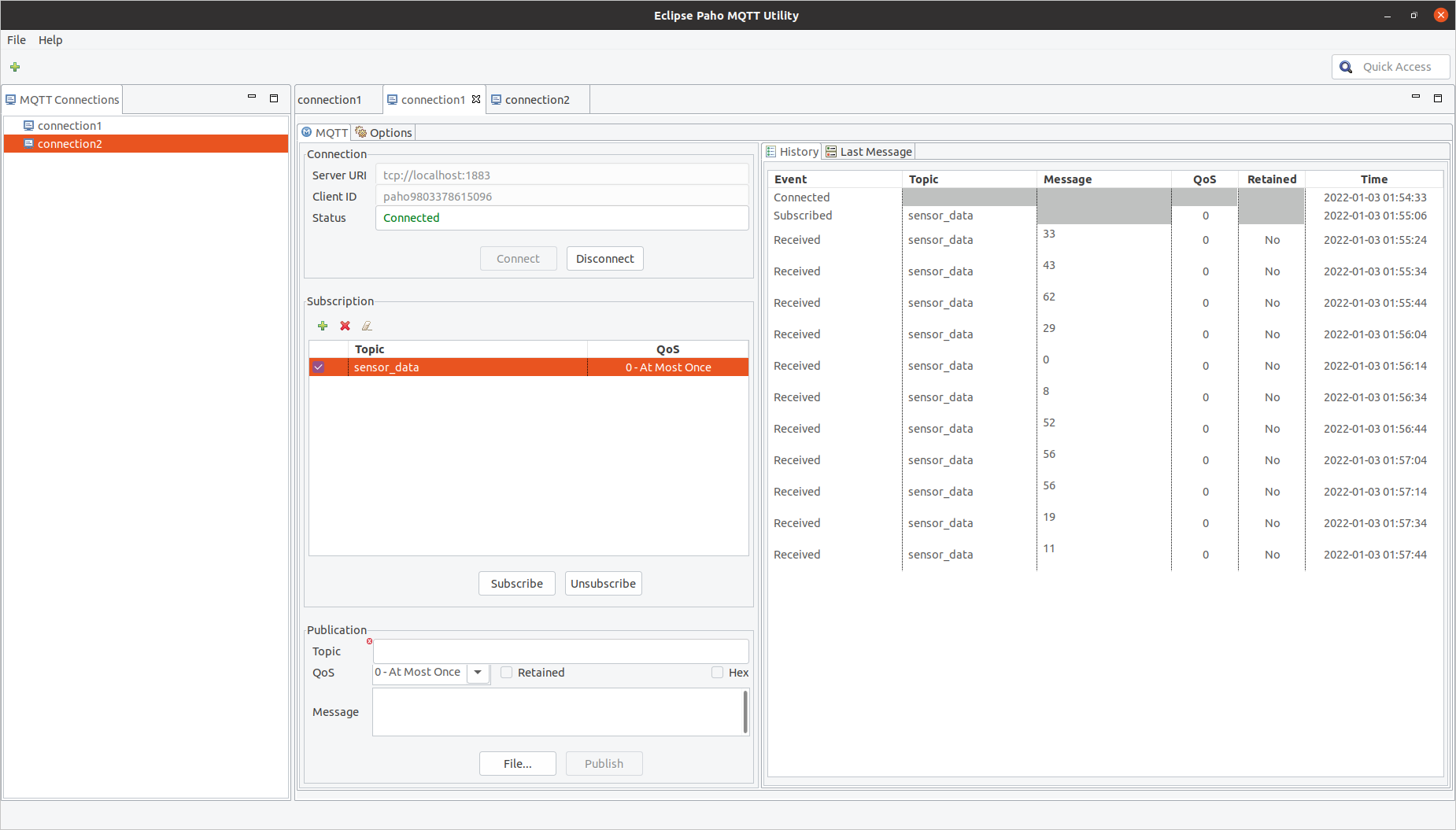
MQTT服务器的搭建相信各位随便搜一下就能解决,就不再赘述。- 总结
本篇是对XR806与MQTT服务器连接实现涉及的相关知识点描述,后续会更改程序相关逻辑以更适合物联网项目,同时后续会再发布一篇Android MQTT客户端的贴(有空的话)。
-
Copyright © 2024 深圳全志在线有限公司 粤ICP备2021084185号 粤公网安备44030502007680号