【全志T113-S3_100ask】5-编写IIC驱动GY-302(twi)
-
前言
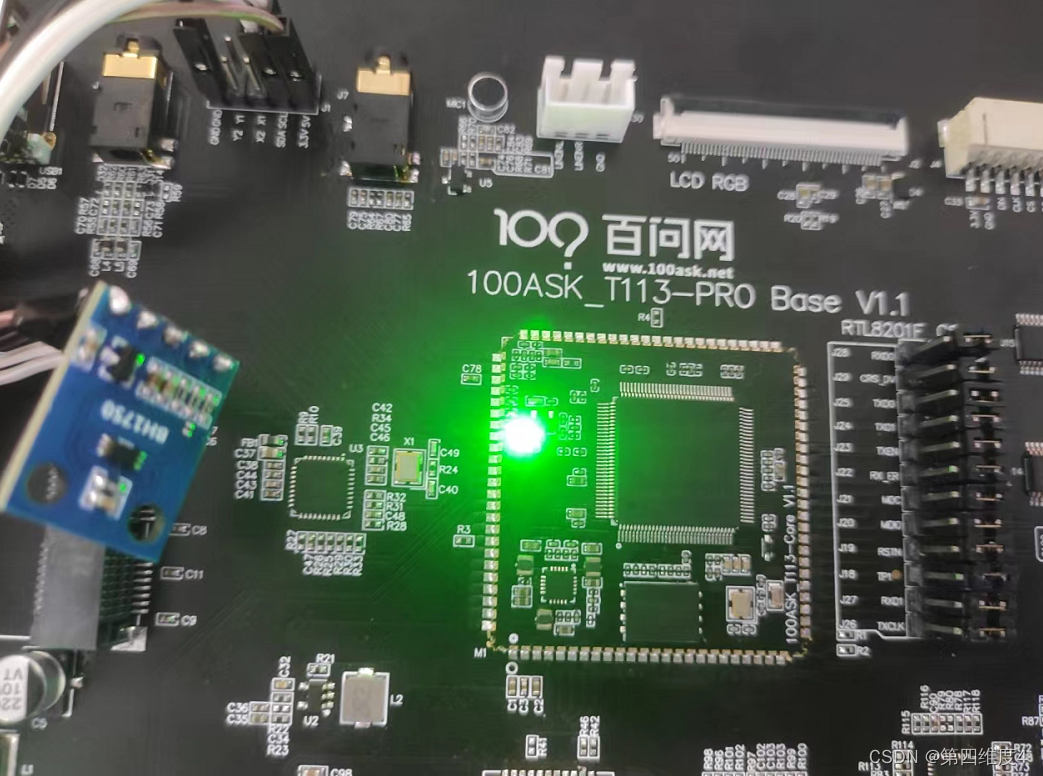
在100ask的板子上预留了一个IIC接口,下面通过这个IIC接口来采集光照强度传感器GY-302(BH1750)。
(一)不使用设备树操作
1、预操作
通过查看设备,我们可以看到上面挂载着一个i2c-2设备,且没有其他的i2c。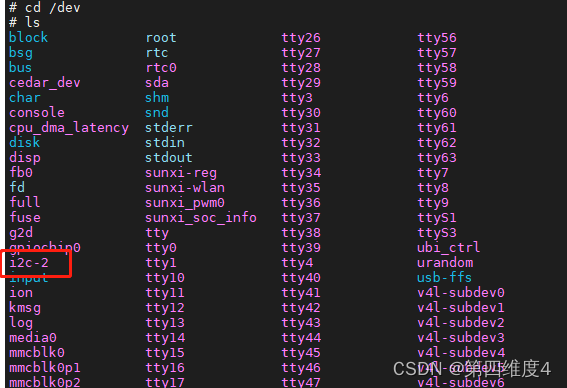
2、使用i2c tools测试iic
i2c-tools编译,安装步骤
/1、下载i2c-tools-4.0 wget https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/software/utils/i2c-tools/i2c-tools-4.0.tar.gz //2、解压 tar -xzvf i2c-tools-4.0.tar.gz //3、修改交叉编译:Makefile中的CC该为使用的交叉编译器 CC ?= arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc //4、编译 Make然后将该工具拷贝到开发板,nfs也好,U盘也行。
然后使用该工具检测设备# ls i2c-tools-4.0 # cd i2c-tools-4.0/ # ls CHANGES Makefile eeprom lib tools COPYING README eepromer py-smbus version.h COPYING.LGPL eeprog include stub # cd tools/ # ls Module.mk i2cdetect.c i2cget i2cset.c util.c i2cbusses.c i2cdetect.o i2cget.8 i2cset.o util.h i2cbusses.h i2cdump i2cget.c i2ctransfer util.o i2cbusses.o i2cdump.8 i2cget.o i2ctransfer.8 i2cdetect i2cdump.c i2cset i2ctransfer.c i2cdetect.8 i2cdump.o i2cset.8 i2ctransfer.o !目前只挂载i2c-2 # i2cdetect -l i2c-2 i2c twi2 I2C adapter # i2cdetect -y 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 20: -- -- -- 23 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --3、编写测试应用
打开设备文件然后设置i2c设备的地址,按照GY-302数据手册中操作流程,连续写0x01和0x11,就可以读出光照信息。
-
初始化 写寄存器0x01 上电
-
设置 0x11 设置成高精度模式 Continuously H-Resolution Mode,即连续高分辨率模式。
-
读数据 unsigned char Buf[3] data=Buf[0]; data=(data<<8)+Buf[1] tmp=data/1.2
#include <stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <linux/i2c-dev.h> #include <errno.h> #define I2C_ADDR 0x23 int main(void) { int fd; char buf[3]; char val, value; float flight; fd = open("/dev/i2c-2", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("打开文件错误:%s\r\n", strerror(errno)); return 1; } if (ioctl(fd, I2C_SLAVE, I2C_ADDR) < 0) { printf("ioctl 错误 : %s\r\n", strerror(errno)); return 1; } val = 0x01; if (write(fd, &val, 1) < 0) { printf("上电失败\r\n"); } val = 0x11; if (write(fd, &val, 1) < 0) { printf("开启高分辨率模式2\r\n"); } usleep(200000); while (1) { if (read(fd, &buf, 3)) { flight = (buf[0] * 256 + buf[1]) * 0.5 / 1.2; printf("光照度: %6.2flx\r\n", flight); } else { printf("读取错误\r\n"); } sleep(3); } }4、测试
# ./iic_gy30_test 光照度: 75.42lx 光照度: 95.14lx 光照度: 311.47lx(二)使用设备树操作
1、TWI 两线串行接口简介
-
在设备树中,找不到任何i2c的节点信息,只找到twi。
TWI(Two-wire Serial Interface)两线串行接口,TWI 完全兼容 I2C 总线。 -
由于TWI总线与传统的I2C总线极其相似。因此不少人误以为TWI总线就是I2C总线,其实这只是一种简单化的理解。TWI总线是对I2C总线的继承和发展。它定义了自已的功能
-
模块和寄存器,寄存器各位功能的定义与I2C总线并不相同;而且TWI总线引入了状奁寄存器,使得TWI总线在操作和使用上比I2C总线更为灵活。
2、添加节点
添加到 &twi2 下
light-sensor@23 { compatible = "gy,bh1750"; reg = <0x23>; };如图所示:
编译烧录后在以下目录可以找得到:
# cd /sys/firmware/devicetree/base/soc@3000000/twi@2502800/ # ls #address-cells compatible interrupts pinctrl-names #size-cells ctp@14 light-sensor@23 reg clock-frequency device_type name resets clock-names dma-names pinctrl-0 status clocks dmas pinctrl-1 #3、编写驱动
#include <linux/ide.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/i2c.h> struct class *class; /* 类 */ int major; /* 主设备号 */ struct i2c_client *gy_sensor_client; // 构造i2c_msg通过这个client调用i2c_tansfer来读写 static int gy_sensor_write_reg(unsigned char addr) { int ret = -1; struct i2c_msg msgs; printk("gy_sensor_client -> addr=%d\n", gy_sensor_client->addr); msgs.addr = gy_sensor_client->addr; // GY302_ADDR,直接封装于i2c_msg msgs.buf = &addr; msgs.len = 1; //长度1 byte msgs.flags = 0; //表示写 ret = i2c_transfer(gy_sensor_client->adapter, &msgs, 1); //这里都封装好了,本来根据i2c协议写数据需要先写入器件写地址,然后才能读 if (ret < 0) { printk("i2c_transfer write err\n"); return -1; } return 0; } static int gy_sensor_read_reg(unsigned char *buf) { int ret = -1; struct i2c_msg msg; msg.addr = gy_sensor_client->addr; // GY30_ADDR msg.buf = buf; msg.len = 2; //长度1 byte msg.flags = I2C_M_RD; //表示读 ret = i2c_transfer(gy_sensor_client->adapter, &msg, 1); //这里都封装好了,本来根据i2c协议读数据需要先写入读地址,然后才能读 if (ret < 0) { printk("i2c_transfer write err\n"); return -1; } return 0; } // 初始化光线传感器 int gy_sensor_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("open gy_sensor\n"); gy_sensor_write_reg(0x01); // power up gy_sensor_write_reg(0x11); return 0; } // 读出传感器的两个字节 static ssize_t gy_sensor_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *off) { unsigned char addr = 0, data[2]; gy_sensor_read_reg(data); copy_to_user(buf, data, 2); return 1; } /* bh1750 操作函数 */ static const struct file_operations gy_sensor_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = gy_sensor_open, .read = gy_sensor_read, }; /* 构造一个platform_driver, 其中的of_match_table字段需要与 light-sensor@23 节点的compatible属性值一致, 当匹配时则调用platform_driver的probe函数 */ static const struct of_device_id ids[] = { {.compatible = "gy,bh1750"}, { } }; // 在i2c_driver的probe函数中得到在总线驱动程序中解析得到的i2c_client, // 并为该光线传感器注册一个字符设备 static int gy_sensor_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id) { gy_sensor_client = client; printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__); major = register_chrdev(0, "gy_sensor", &gy_sensor_fops); class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "gy_sensor"); device_create(class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "gy_sensor"); /* /dev/gy_sensor */ return 0; } // 在platform_driver的remove函数中,注销该字符设备 static int gy_sensor_remove(struct i2c_client *client) { device_destroy(class, MKDEV(major, 0)); class_destroy(class); unregister_chrdev(major, "gy_sensor"); return 0; } /* 分配/设置i2c_driver */ static struct i2c_driver gy_sensor_driver = { .driver = { .name = "bh1750", .owner = THIS_MODULE, .of_match_table = ids, }, .probe = gy_sensor_probe, .remove = gy_sensor_remove, }; /* * @description : 驱动入口函数 */ static int __init bh1750_init(void) { int ret = 0; ret = i2c_add_driver(&gy_sensor_driver); return ret; } /* * @description : 驱动出口函数 */ static void __exit bh1750_exit(void) { i2c_del_driver(&gy_sensor_driver); } /* module_i2c_driver(bh1750_driver) */ module_init(bh1750_init); module_exit(bh1750_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("zhu");4、编写测试程序
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { int fd; char val; unsigned char buf[3]; float flight; fd = open("/dev/gy_sensor", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("can't open /dev/gy_sensor\n"); return -1; } usleep(200000); while(1) { if(read(fd,&buf,3)){ flight=(buf[0]*256+buf[1])*0.5/1.2; printf("light: %6.2flx\r\n",flight); } else{ printf("read err!\r\n"); } sleep(4); } return 0; }5、测试
加载驱动
# insmod iic_gy302_dts.ko [ 62.979905] iic_gy302_dts: loading out-of-tree module taints kernel. [ 62.988058] /disk/vsCode/09_iic_gy302_dts/iic_gy302_dts.c gy_sensor_probe 120 # lsmod Module Size Used by Tainted: G iic_gy302_dts 16384 0 sunxi_ce 57344 0采集数据
# ./iic_gy302_dts_test [ 164.872116] open gy_sensor [ 164.875291] gy_sensor_client -> addr=35 [ 164.879870] gy_sensor_client -> addr=35 light: 46.67lx light: 46.25lx light: 40.42lx light: 61.67lx light: 65.42lx light: 2098.33lx light: 4914.17lx light: 17047.50lx light: 40.83lx light: 40.42lx测试完成。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_46079439/article/details/126005394
-
Copyright © 2024 深圳全志在线有限公司 粤ICP备2021084185号 粤公网安备44030502007680号