【BIGTREETECH PI 全志H616开发板】多媒体开发应用
-
本文转载自:http://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/thread-1249107-1-1.html
原文作者@qinyunti前言
本开发板接口资源丰富,支持HDMI,板子虽小但是五脏俱全性能强大。
特别适合多媒体终端的开发,本片演示基于ffmpeg进行多媒体开发,实现网络视频播放的Demo。
ffmpeg安装
由于系统运行的ubuntu所以系统就自带了ffmpeg,如果没有则可以sudo apt-get install ffmpeg安装,前提是已经按照之前配置好了wifi可以联网。
wget https://github.com/BtbN/FFmpeg-B ... 4-gpl-shared.tar.xz sudo apt-get install xz-utils xz -d ffmpeg-master-latest-linuxARM64-gpl-shared.tar.xz tar -xvf ffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared.tarFfmpeg性能测试
下载测试文件wget
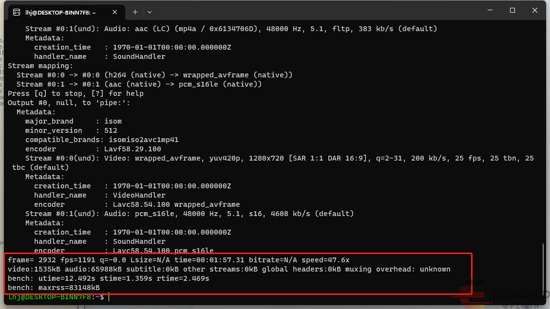
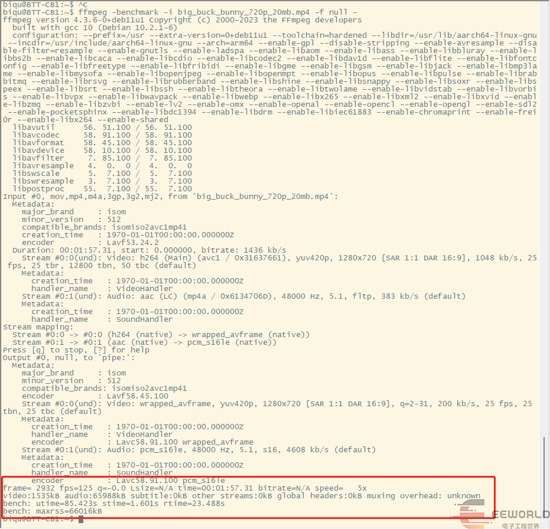
ffmpeg -benchmark -i big_buck_bunny_720p_20mb.mp4 -f null -分别在WSL和开发板中运行对比性能大概差10倍左右
WSL中
开发板中
Ffmpeg代码开发
编码测试
vi encode_video.c代码如下
#include #include #include #include #include #include static void encode(AVCodecContext *enc_ctx, AVFrame *frame, AVPacket *pkt, FILE *outfile) { int ret; /* send the frame to the encoder */ if (frame) printf("Send frame %3"PRId64"\n", frame->pts); ret = avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame); if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Error sending a frame for encoding\n"); exit(1); } while (ret >= 0) { ret = avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, pkt); if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) return; else if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Error during encoding\n"); exit(1); } printf("Write packet %3"PRId64" (size=%5d)\n", pkt->pts, pkt->size); fwrite(pkt->data, 1, pkt->size, outfile); av_packet_unref(pkt); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { const char *filename, *codec_name; const AVCodec *codec; AVCodecContext *c= NULL; int i, ret, x, y; FILE *f; AVFrame *frame; AVPacket *pkt; uint8_t endcode[] = { 0, 0, 1, 0xb7 }; if (argc <= 2) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s \n", argv[0]); exit(0); } filename = argv[1]; codec_name = argv[2]; /* find the mpeg1video encoder */ codec = avcodec_find_encoder_by_name(codec_name); if (!codec) { fprintf(stderr, "Codec '%s' not found\n", codec_name); exit(1); } c = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec); if (!c) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video codec context\n"); exit(1); } pkt = av_packet_alloc(); if (!pkt) exit(1); /* put sample parameters */ c->bit_rate = 400000; /* resolution must be a multiple of two */ c->width = 352; c->height = 288; /* frames per second */ c->time_base = (AVRational){1, 25}; c->framerate = (AVRational){25, 1}; /* emit one intra frame every ten frames * check frame pict_type before passing frame * to encoder, if frame->pict_type is AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I * then gop_size is ignored and the output of encoder * will always be I frame irrespective to gop_size */ c->gop_size = 10; c->max_b_frames = 1; c->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P; if (codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264) av_opt_set(c->priv_data, "preset", "slow", 0); /* open it */ ret = avcodec_open2(c, codec, NULL); if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not open codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret)); exit(1); } f = fopen(filename, "wb"); if (!f) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s\n", filename); exit(1); } frame = av_frame_alloc(); if (!frame) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video frame\n"); exit(1); } frame->format = c->pix_fmt; frame->width = c->width; frame->height = c->height; ret = av_frame_get_buffer(frame, 0); if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the video frame data\n"); exit(1); } /* encode 1 second of video */ for (i = 0; i < 25; i++) { fflush(stdout); /* Make sure the frame data is writable. On the first round, the frame is fresh from av_frame_get_buffer() and therefore we know it is writable. But on the next rounds, encode() will have called avcodec_send_frame(), and the codec may have kept a reference to the frame in its internal structures, that makes the frame unwritable. av_frame_make_writable() checks that and allocates a new buffer for the frame only if necessary. */ ret = av_frame_make_writable(frame); if (ret < 0) exit(1); /* Prepare a dummy image. In real code, this is where you would have your own logic for filling the frame. FFmpeg does not care what you put in the frame. */ /* Y */ for (y = 0; y < c->height; y++) { for (x = 0; x < c->width; x++) { frame->data[0][y * frame->linesize[0] + x] = x + y + i * 3; } } /* Cb and Cr */ for (y = 0; y < c->height/2; y++) { for (x = 0; x < c->width/2; x++) { frame->data[1][y * frame->linesize[1] + x] = 128 + y + i * 2; frame->data[2][y * frame->linesize[2] + x] = 64 + x + i * 5; } } frame->pts = i; /* encode the image */ encode(c, frame, pkt, f); } /* flush the encoder */ encode(c, NULL, pkt, f); /* Add sequence end code to have a real MPEG file. It makes only sense because this tiny examples writes packets directly. This is called "elementary stream" and only works for some codecs. To create a valid file, you usually need to write packets into a proper file format or protocol; see mux.c. */ if (codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO || codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO) fwrite(endcode, 1, sizeof(endcode), f); fclose(f); avcodec_free_context(&c); av_frame_free(&frame); av_packet_free(&pkt); return 0; }编译
gcc encode_video.c -Iffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared/include -Lffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared/lib -lavcodec -lavutil -lswresample -o encode运行
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/root/ffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./encode encode.bin mpeg1video播放编码的文件
ffplay.exe -i encode.bin
解码测试
vi decode_video.c代码如下
#include #include #include #include #define INBUF_SIZE 4096 static void pgm_save(unsigned char* buf, int wrap, int xsize, int ysize, char* filename) { FILE* f; int i; f = fopen(filename, "wb"); fprintf(f, "P5\n%d %d\n%d\n", xsize, ysize, 255); for (i = 0; i < ysize; i++) fwrite(buf + i * wrap, 1, xsize, f); fclose(f); } static void decode(AVCodecContext* dec_ctx, AVFrame* frame, AVPacket* pkt, const char* filename) { char buf[1024]; int ret; ret = avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, pkt); if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Error sending a packet for decoding\n"); exit(1); } while (ret >= 0) { ret = avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame); if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) return; else if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Error during decoding\n"); exit(1); } printf("saving frame %3"PRId64"\n", dec_ctx->frame_num); fflush(stdout); /* the picture is allocated by the decoder. no need to free it */ snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%s-%"PRId64, filename, dec_ctx->frame_num); pgm_save(frame->data[0], frame->linesize[0], frame->width, frame->height, buf); } } int main(int argc, char** argv) { const char* filename, * outfilename; const AVCodec* codec; AVCodecParserContext* parser; AVCodecContext* c = NULL; FILE* f; AVFrame* frame; uint8_t inbuf[INBUF_SIZE + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE]; uint8_t* data; size_t data_size; int ret; int eof; AVPacket* pkt; if (argc <= 2) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s \n" "And check your input file is encoded by mpeg1video please.\n", argv[0]); exit(0); } filename = argv[1]; outfilename = argv[2]; pkt = av_packet_alloc(); if (!pkt) exit(1); /* set end of buffer to 0 (this ensures that no overreading happens for damaged MPEG streams) */ memset(inbuf + INBUF_SIZE, 0, AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE); /* find the MPEG-1 video decoder */ codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO); if (!codec) { fprintf(stderr, "Codec not found\n"); exit(1); } parser = av_parser_init(codec->id); if (!parser) { fprintf(stderr, "parser not found\n"); exit(1); } c = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec); if (!c) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video codec context\n"); exit(1); } /* For some codecs, such as msmpeg4 and mpeg4, width and height MUST be initialized there because this information is not available in the bitstream. */ /* open it */ if (avcodec_open2(c, codec, NULL) < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not open codec\n"); exit(1); } f = fopen(filename, "rb"); if (!f) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s\n", filename); exit(1); } frame = av_frame_alloc(); if (!frame) { fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video frame\n"); exit(1); } do { /* read raw data from the input file */ data_size = fread(inbuf, 1, INBUF_SIZE, f); if (ferror(f)) break; eof = !data_size; /* use the parser to split the data into frames */ data = inbuf; while (data_size > 0 || eof) { ret = av_parser_parse2(parser, c, &pkt->data, &pkt->size, data, data_size, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, 0); if (ret < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Error while parsing\n"); exit(1); } data += ret; data_size -= ret; if (pkt->size) decode(c, frame, pkt, outfilename); else if (eof) break; } } while (!eof); /* flush the decoder */ decode(c, frame, NULL, outfilename); fclose(f); av_parser_close(parser); avcodec_free_context(&c); av_frame_free(&frame); av_packet_free(&pkt); return 0; }编译
gcc decode_video.c -Iffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared/include -Lffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared/lib -lavcodec -lavutil -lswresample -o decode运行
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/root/ffmpeg-master-latest-linuxarm64-gpl-shared/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH ./decode encode.bin decode.bin网络视频播放
PC上从以下地址下载VLC安装https://www.videolan.org/vlc/
电脑上确认IP地址我这里是192.168.31.64
开发板上运行
ffmpeg -re -i big_buck_bunny_720p_20mb.mp4 -an -vcodec copy -f rtp rtp://192.168.31.64:5004打印如下,复位红色框中的内容,不包括SDP:这一行
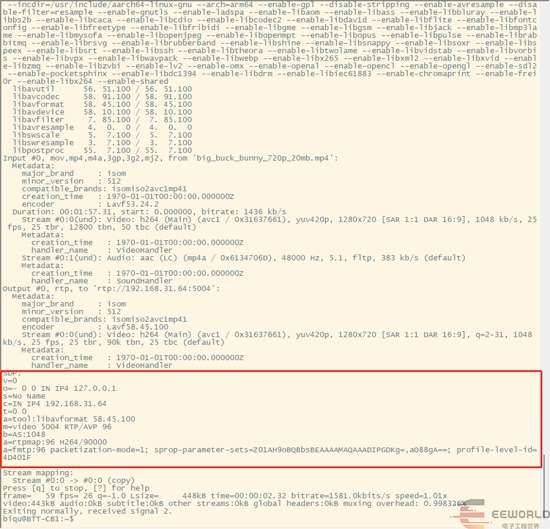
PC上新建demo.sdp文件,黏贴上述内容
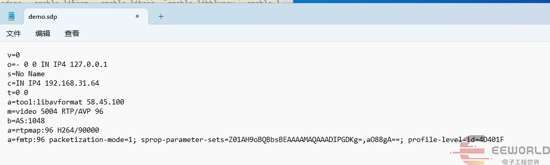
右键点击demo.sdp使用VLC打开
即可看到开始播放视频

总结
得益于开发板强劲的性能和运行完整的Ubuntu系统环境,可以方便的进行多媒体相关的开发。
Copyright © 2024 深圳全志在线有限公司 粤ICP备2021084185号 粤公网安备44030502007680号