【随笔记】C++ condition_variable 陷阱
-
问题说明
通过 std::condition_variable 来实现超时等待,会受到系统时间变化的影响,系统时间倒退修改就会导致延后唤醒,系统时间提前将会导致提前被唤醒,返回结果仍为超时。
这种问题只有在系统时间发生变化的时候才会出现,例如搭配 NTP 更新功能,硬件还未同步时间时,一般在 1993 年,此时使用了 wait_for() 这类接口等待 10 秒,结果在 10 秒内被 ntp 同步更新了时间到 2023,那么时间生效的一瞬间,wait_for() 就会直接被唤醒,且返回的结果是超时唤醒。
另外一种时间倒退的场景,则影响会更大,例如在 2023 年,时间调回了 2022 年,那么 wait_for() 将会等待一年多才会被超时唤醒,代码执行的现象就像是调用了 wait() 的效果。
通过分析 std::condition_variable 源码,可以很清晰看到使用的是系统时间:
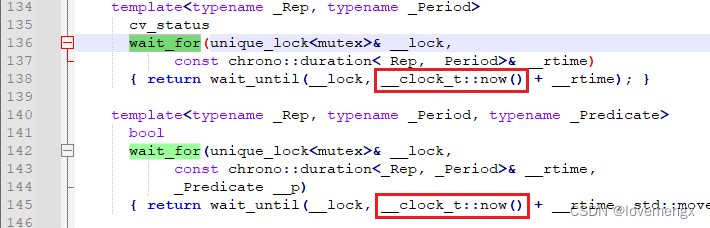
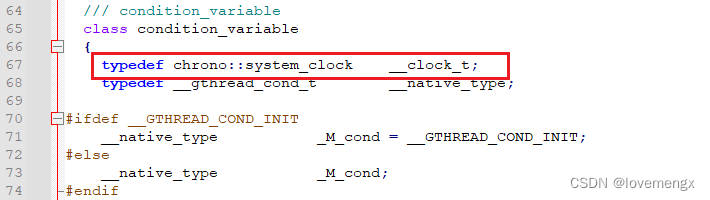
示例代码:
实现一个可以随时被打断的延时等待类。
有隐患的代码:
bool DelayControl::delay(unsigned int millisecond) { bool is_timeout = false; unique_lock< mutex > lock(mutex_data_); is_runing_ = true; is_timeout = (cv_status::timeout == cond_.wait_for(lock, chrono::milliseconds(millisecond))); is_runing_ = false; lock.unlock(); return is_timeout; } void DelayControl::stop() { unique_lock< mutex > lock(mutex_data_); cond_.notify_all(); }改进方案一(使用 select 方式实现):缺点是一个对象会浪费两个文件描述符资源
DelayControl::DelayControl() { is_runing_ = false; pipe(pipefd_); } bool DelayControl::delay(unsigned int millisecond) { int result; fd_set rdfs; struct timeval timeout; bool is_timeout = false; is_runing_ = true; FD_ZERO(&rdfs); FD_SET(pipefd_[0], &rdfs); timeout.tv_sec = millisecond / 1000; timeout.tv_usec = (millisecond - ((millisecond / 1000) * 1000)) * 1000; switch((result = select(pipefd_[1] + 1, &rdfs, NULL, NULL, &timeout))){ case 0: is_timeout = true; break; } is_runing_ = false; return is_timeout; } void DelayControl::stop() { write(pipefd_[1], "", 1); }改进方案二(使用 pthread_cond_timedwait 方式实现):完美方案
关键在于使用了 CLOCK_MONTONIC ,其用不是系统时间,而是内核的计数器 jiffies,系统每次启动时,jiffies初始化为0。每来一个timer interrupt,jiffies加1,即它代表系统启动后流逝的tick数,jiffies 只会单调递增。
DelayControl::DelayControl() { is_runing_ = false; pthread_condattr_init(&cond_cattr_); pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_data_, NULL); pthread_condattr_setclock(&cond_cattr_, CLOCK_MONOTONIC); pthread_cond_init(&cond_, &cond_cattr_); } DelayControl::~DelayControl() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_data_); pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond_); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_data_); pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_data_); } bool DelayControl::delay(unsigned int millisecond) { struct timespec tv; bool is_timeout = false; pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_data_); is_runing_ = true; clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &tv); millisecond += (tv.tv_sec * 1000) + (tv.tv_nsec / 1000000); tv.tv_sec = millisecond / 1000; tv.tv_nsec = (millisecond - ((millisecond / 1000) * 1000)) * 1000 * 1000; is_timeout = pthread_cond_timedwait(&cond_, &mutex_data_, &tv) ? true : false; is_runing_ = false; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_data_); return is_timeout; } bool DelayControl::isRuning() { bool is_runing = false; pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_data_); is_runing = is_runing_; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_data_); return is_runing; } void DelayControl::stop() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_data_); pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond_); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_data_); }用如下随机设置系统时间的方式压力测 6 小时通过:
#define RAND(_MIN_, _MAX_) (rand() % (_MAX_-_MIN_+1) + _MIN_) int main() { Logger::getInstance().init("/mnt/UDISK/pre_bullying/logs/DelayControl.log", 1024*1024*2, 1); std::shared_ptr<MeasureTime> sp_timer_; std::shared_ptr<DelayControl> sp_delay_; sp_delay_ = std::make_shared<DelayControl>(); sp_timer_ = std::make_shared<MeasureTime>(100); srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); { DelayControl mDelayControl; mDelayControl.delay(1000); } std::thread t([&]{ char buf[64] = {0}; while(true){ usleep(RAND(0, 5000) * 1000); system("ntpclient -s -c 1 -h ntp7.aliyun.com -i 3"); usleep(RAND(0, 5000) * 1000); snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "date -s \"%.4d-%.2d-%.2d %.2d:%.2d:%.2d\"", RAND(1990, 2030), RAND(1, 12), RAND(1, 29), RAND(0, 23), RAND(1, 60), RAND(1, 60)); iprint("set time:[%s]", buf); system(buf); } }); t.detach(); while(true) { int delay = RAND(0, 5000); unsigned long long ms = 0; iprint("delay:-->[%d]", delay); sp_timer_->update(); bool isdone = sp_delay_->delay(delay); ms = sp_timer_->getMillisecond(); iprint("delay %s:[%d][%d][%lld]", delay != ms ? "delay != ms" : "done", isdone, delay, sp_timer_->getMillisecond()); } return 0; } -
linux下的ipc阻塞超时时间的计算好像也是这样。涉及到更新时间的应用搭配超时相关都要小心,处理好其中的逻辑
Copyright © 2024 深圳全志在线有限公司 粤ICP备2021084185号 粤公网安备44030502007680号